function Get-NetshSetup($sslBinding='0.0.0.0:443') {
$sslsetup = netsh http show ssl 0.0.0.0:443
#Get-Member -InputObject $sslsetup
$sslsetupKeys = @{}
foreach ($line in $sslsetup){
if ($line -ne $null -and $line.Contains(': ')){
$key = $line.Split(':')[0]
$value = $line.Split(':')[1]
if (!$sslsetupKeys.ContainsKey($key)){
$sslsetupKeys.Add($key.Trim(), $value.Trim())
}
}
}
return $sslsetup
}
function Display-NetshSetup($sslBinding='0.0.0.0:443'){
Write-Host SSL-Setup is:
$sslsetup = Get-NetshSetup($sslBinding)
foreach ($key in $sslsetup){
Write-Host $key $sslsetup[$key]
}
}
function Modify-NetshSetup($sslBinding='0.0.0.0:443', $certstorename='My',
$verifyclientcertrevocation='disable', $verifyrevocationwithcachedcleintcertonly='disable',
$clientCertNegotiation='enable', $dsmapperUsage='enable'){
$sslsetup = Get-NetshSetup($sslBinding)
echo Deleting sslcert netsh http binding for $sslBinding ...
netsh http delete sslcert ipport=$sslBinding
echo Adding sslcert netsh http binding for $sslBinding...
netsh http add sslcert ipport=$sslBinding certhash=$sslsetup['Certificate Hash'] appid=$sslsetup['Application ID'] certstorename=$certstorename verifyclientcertrevocation=$verifyclientcertrevocation verifyrevocationwithcachedclientcertonly=$verifyrevocationwithcachedcleintcertonly clientcertnegotiation=$clientCertNegotiation dsmapperusage=$dsmapperUsage
echo Done. Inspect output.
Display-NetshSetup $sslBinding
}
function Add-NetshSetup($sslBinding, $certstorename, $certhash, $appid,
$verifyclientcertrevocation='disable', $verifyrevocationwithcachedcleintcertonly='disable',
$clientCertNegotiation='enable', $dsmapperUsage='enable'){
echo Adding sslcert netsh http binding for $sslBinding...
netsh http add sslcert ipport=$sslBinding certhash=$certhash appid=$appid clientcertnegotiation=$clientCertNegotiation dsmapperusage=$dsmapperUsage certstorename=$certstorename verifyclientcertrevocation=$verifyclientcertrevocation verifyrevocationwithcachedclientcertonly=$verifyrevocationwithcachedcleintcertonly
echo Done. Inspect output.
Display-NetshSetup $sslBinding
}
#Get-NetshSetup('0.0.0.0:443');
Display-NetshSetup
#Modify-NetshSetup
Add-NetshSetup '0.0.0.0:443' 'MY' 'c0fe06da89bcb8f22da8c8cbdc97be413b964619' '{4dc3e181-e14b-4a21-b022-59fc669b0914}'
Display-NetshSetup
Wednesday, 17 October 2018
Working with Netsh http sslcert setup and SSL bindings through Powershell
I am working with a solution at work where I need to enable IIS Client certificates. I am not able to get past the "Provide client certificate" dialog, but
it is possible to alter the setup of SSL cert bindings on your computer through the Netsh command. This command is not in Powershell, but at the command line.
I decided to write some Powershell functions to be able to alter this setup atleast in an easier way. One annoyance with the netsh command is that you have to keep track of the
Application Id and Certificate hash values. Here, we can easier keep track of this through Powershell code.
The Powershell code to display and alter, modify, delete and and SSL cert bindings is as follows:
Saturday, 29 September 2018
Injecting text in html lists into lists using Sass
I wanted to test out if I could inject text via Sass style sheets to see if Sass could somehow support this. Of course, this is already possible in CSS using the nth-child selector and the ::after selector.
Here is a sample of the technique used in this article!
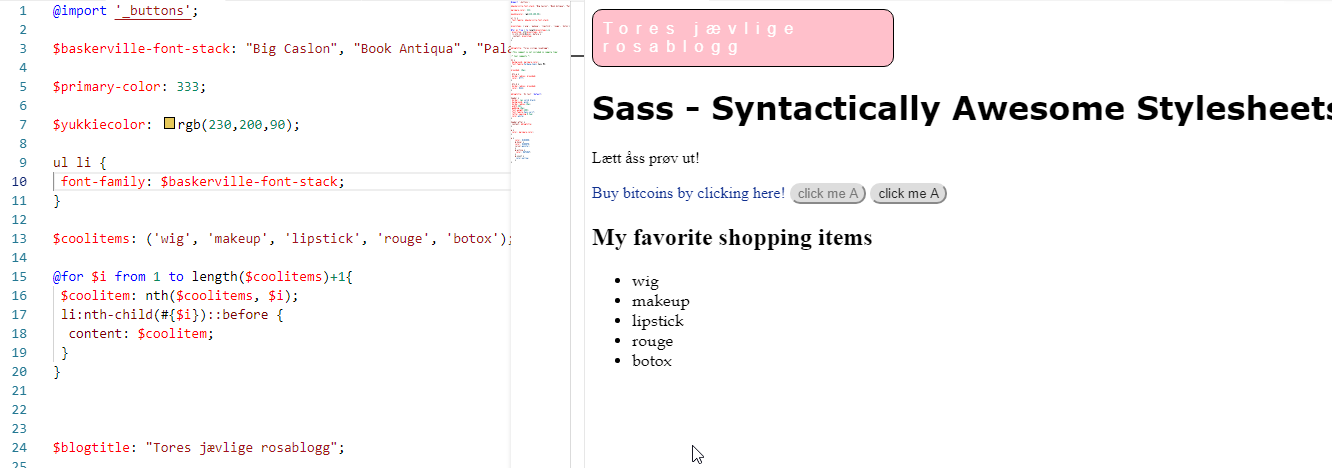 In Sass, however, we can inject text into a large list if we want. This means that the DOM must support the data you want to inject, if you want to inject for example five strings into an array of <ul>
of <li> items, you must also have five items of <li>
Anyways, this is what I ended up with:
In Sass, however, we can inject text into a large list if we want. This means that the DOM must support the data you want to inject, if you want to inject for example five strings into an array of <ul>
of <li> items, you must also have five items of <li>
Anyways, this is what I ended up with:
 In Sass, however, we can inject text into a large list if we want. This means that the DOM must support the data you want to inject, if you want to inject for example five strings into an array of <ul>
of <li> items, you must also have five items of <li>
Anyways, this is what I ended up with:
In Sass, however, we can inject text into a large list if we want. This means that the DOM must support the data you want to inject, if you want to inject for example five strings into an array of <ul>
of <li> items, you must also have five items of <li>
Anyways, this is what I ended up with:
$baskerville-font-stack: "Big Caslon", "Book Antiqua", "Palatino Linotype", Georgia, serif !default;
ul li {
font-family: $baskerville-font-stack;
}
$coolitems: ('wig', 'makeup', 'lipstick', 'rouge', 'botox');
@for $i from 1 to length($coolitems)+1{
$coolitem: nth($coolitems, $i);
li:nth-child(#{$i})::before {
content: $coolitem;
}
}
$blogtitle: "Tores jævlige rosablogg";
We first declare an array in Sass using $coolitems: ('wig', 'makeup', 'lipstick', 'rouge', 'botox'). We then use the @for loop in Sass to get loop through this array. The syntax is:
@for $i from 1 to length($coolarray)+1 I had to use the +1 here in my sample.. Then we grab hold of the current item using the nth function, passing in the array $coolitems and specifying the index $i. Now that we have the
item of the $coolitems array, we can set the content CSS property of the n-th child and use the ::before (or ::after) selector. I tried to avoid using the +1 in the for loop, but then the last item of my array was not included in the list.
Note - the use of the #{$i} in the syntax above. This is called variable interpolation in Sass. It is similar syntax-wise to variable interpolation in shell scripts, actually. We use it so that we can refer to the variable $i inside the nth-child operator of CSS selector.
And the nth operator is as noted used to grab hold of the nth item of the Sass array.
And your HTML will then look like this:
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
So you actually now have a list in HTML which is empty, but the values are injected through CSS! And Sass makes supporting such scenarios easier. Now why the heck would you want such a thing? I do not know,
I am more a backend developer than webdev frontend developer, it is though cool that you can load up data into the DOM using Sass and CSS
Thursday, 6 September 2018
Some handy Git tips - show latest commits and searching the log and more
This article will present some tips around Git and how you can add functionality for showing the latest commits and search the log.
I would like to search these aliased command to show you how they can ease your everyday use of Git from the commandline.
[alias]
glog = log --all --decorate --oneline --graph
glogf = log --all --decorate --oneline --graph --pretty=fuller
st = status
out = !git fetch && git log FETCH_HEAD..
outgoing = !git fetch && git log FETCH_HEAD..
in = !git fetch && git log ..FETCH_HEAD
incoming = !git fetch && git log ..FETCH_HEAD
com = "!w() { git commit --all --message \"$1\"; }; w"
undopush = "!w() { git revert HEAD~\"$1\"..HEAD; }; w"
searchlog = "!f() { git --no-pager log --color-words --all --decorate --graph -i --grep \"$1\"; }; f"
branches = branch --verbose --sort=-committerdate --format '%(HEAD)%(color:yellow)%(refname:short)%(color:reset) -%(color:red)%(objectname:short)%(color:reset) - %(contents:subject) -%(authorname) (%(color:green)%(committerdate:relative)%(color:reset))'
allbranches = "!g() { git branch --all --verbose --sort=-committerdate --format '%(HEAD) %(color:yellow)%(refname:short)%(color:reset) -%(color:red)%(objectname:short)%(color:reset) - %(contents:subject) -%(authorname) (%(color:green)%(committerdate:relative)%(color:reset))' --color=always | less -R; }; g"
verify = fsck
clearlocal = clean -fd && git reset
stash-unapply = !git stash show -p | git apply -R
lgb = log --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset%n' --abbrev-commit --date=relative --branches tree = log --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset%n' --abbrev-commit --date=relative --branches alltree = log --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset%n' --date=relative --branches --all
latest = "!f() { echo "Latest \"${1:-11}\" commits accross all branches:"; git log --abbrev-commit --date=relative --branches --all --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset%n' -n ${1:-11}; } ; f"
add-commit = !git add -A && git commit
showconfig = config --global -e
[merge]
tool = kdiff3
[mergetool "kdiff3"]
cmd = \"C:\\\\Program Files\\\\KDiff3\\\\kdiff3\" $BASE $LOCAL $REMOTE -o $MERGED [core]
editor = 'c:/program files/sublime text 3/subl.exe' -w
[core]
editor = 'c:/Program Files/Sublime Text 3/sublime_text.exe'
The best aliases are how you set up Sublime Text 3 as the Git editor and also how you can show the latest commits. The latest commits use a parametrized shell function. I set the default value to 11 in this case, if you do not give a parameter. You can for example show the latest 2 commits by typing: git latest 2
latest = "!f() { echo "Latest \"${1:-11}\" commits accross all branches:"; git log --abbrev-commit --date=relative --branches --all --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset%n' -n ${1:-11}; } ; f"
Note the use of a shell function and also that we refer to the first parameter as ${1} i bash shell script, with a :-11 to set the first param as 11.
The syntax is ${n:-p} where n is the nth parameter (not starting with zero!) and p is the default value. A special syntax, but that is how bash works. Also note that a git alias with a shell function can do multiple functions, separated with semi-colon ;.
The searchlog alias / shell function is also handy:
searchlog = "!f() { git --no-pager log --color-words --all --decorate --graph -i --grep \"$1\"; }; f"
Also, multiple aliases here are similar to Mercurial's in and out commands to detect incoming pushed commits and outgoing local commits.
Happy Git-ing!
Tuesday, 21 August 2018
Creating a validation attribute for multiple enum values in C#
This article will present a validation attribute for multiple enum value in C#. In C#, generics is not supported in attributes.
The following class therefore specifyes the type of enum and provides a list of invalid enum values as an example of such an attribute.

using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ValidateEnums
{
public sealed class InvalidEnumsAttribute : ValidationAttribute
{
private List<object> _invalidValues = new List<object>();
public InvalidEnumsAttribute(Type enumType, params object[] enumValues)
{
foreach (var enumValue in enumValues)
{
var _invalidValueParsed = Enum.Parse(enumType, enumValue.ToString());
_invalidValues.Add(_invalidValueParsed);
}
}
public override bool IsValid(object value)
{
foreach (var invalidValue in _invalidValues)
{
if (Enum.Equals(invalidValue, value))
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
Let us make use of this attribute in a sample class.
public class Snack
{
[InvalidEnums(typeof(IceCream), IceCream.None, IceCream.All )]
public IceCream IceCream { get; set; }
}
We can then test out this attribute easily in NUnit tests for example:
[TestFixture]
public class TestEnumValidationThrowsExpected
{
[Test]
[ExpectedException(typeof(ValidationException))]
[TestCase(IceCream.All)]
[TestCase(IceCream.None)]
public void InvalidEnumsAttributeTest_ThrowsExpected(IceCream iceCream)
{
var snack = new Snack { IceCream = iceCream };
Validator.ValidateObject(snack, new ValidationContext(snack, null, null), true);
}
[Test]
public void InvalidEnumsAttributeTest_Passes_Accepted()
{
var snack = new Snack { IceCream = IceCream.Vanilla };
Validator.ValidateObject(snack, new ValidationContext(snack, null, null), true);
Assert.IsTrue(true, "Test passed for valid ice cream!");
}

Sunday, 19 August 2018
ConfigurationManager for .Net Core
.Net Core is changing a lot of the underlying technology for .Net developers migrating to this development environment. System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager class is gone and web.config and app.config
files, which are XML-based are primrily replaced with .json files, at least in Asp.NET Core 2 for example.
Let's look at how we can implement a class to let you at least be able to read AppSettings in your applicationSettings.json file which can be later refined. This implementation is my first version.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
namespace WebApplication1
{
public static class ConfigurationManager
{
private static IConfiguration _configuration;
private static string _basePath;
private static string[] _configFileNames;
public static void SetBasePath(IHostingEnvironment hostingEnvironment)
{
_basePath = hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath;
_configuration = null;
//fix base path
_configuration = GetConfigurationObject();
}
public static void SetApplicationConfigFiles(params string[] configFileNames)
{
_configFileNames = configFileNames;
}
public static IConfiguration AppSettings
{
get
{
if (_configuration != null)
return _configuration;
_configuration = GetConfigurationObject();
return _configuration;
}
}
private static IConfiguration GetConfigurationObject()
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(_basePath ?? Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
if (_configFileNames != null && _configFileNames.Any())
{
foreach (var configFile in _configFileNames)
{
builder.AddJsonFile(configFile, true, true);
}
}
else
builder.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", false, true);
return builder.Build();
}
}
}
We can then easily get app settings from our config file:
string endPointUri = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["EmployeeWSEndpointUri"];Sample appsettings.json file:
{
"Logging": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"Debug": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
},
"Console": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
}
},
"EmployeeWSEndpointUri": "https://someserver.somedomain.no/someproduct/somewcfservice.svc"
}
If you have nested config settings, you can refer to these using the syntax SomeAppSetting:SomeSubAppSetting, like "Logging:Debug:LogLevel:Default".
Creating a VM in Azure with Powershell core in Linux
This article will describe how a virtual machine in Azure from a command line in Linux. Powershell core will be used and I have tested this procedure using the Linux distribution MX-17 Horizon.
First, we will update the package list for APT (Advanced Packaging Tool), get the latest versions of cURL and apt-transport-https and add the
GPG key for the Microsoft repository for Powershell core. Then APT is once more updated and the package powershell is installed. The following script works on Debian-based distributions:
The last command is executed to check that the Powershell module is available. Type [Y] to allow the module installation in the first step. Next off, logging into the Azure Resource Manager. Type the following command in Powershell core:
sudo apt-get install
sudo apt-get install curl apt-transport-https
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/microsoft-debian-jessie-prod jessie main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list'
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y powershell
On my system however, I need to make use of Snap packages. This is because MX-Horizon fails to install powershell due to restrictions on libssl1.0 and libicu52.
Anyways this route let me start up Powershell on MX-17 Horizon:
sudo apt-get install snapd
sudo snap install powershell-preview --classic
sudo snap run powershell-preview
Logging into Azure RM account
Running powershell-preview allows you to both run Powershell commands such as Get-ChildItem ("ls") and Unix tools such as ls (!) from the Powershell command line. We will first install the Powershell module AzureRM.NetCore inside the Powershell session, which is running.
Install-Module AzureRM.Netcore
Get-Command -Module AzureRM.Compute.Netcore
The last command is executed to check that the Powershell module is available. Type [Y] to allow the module installation in the first step. Next off, logging into the Azure Resource Manager. Type the following command in Powershell core:
Login-AzureRMAccount
Running this command will prompt a code and tell you to open up a browser window and log on to: https://microsoft.com/devicelogin
Then you log in to your Azure account and if you are successfully logged in, your Powershell core session is authenticated and you can access your Azure account and its resources!
Creating the Virtual machine in Azure
Creating the virtual machine is done in several steps. The script below is to be saved into a Powershell script file, forexample AzureVmCreate.ps1. There are many steps involved into establishing an installation of a VM in Azure. We will in this sample set up all the necessities to get an Ubuntu Server LTS. If you already have got for example a resource group in Azure, the script below can use this resource group instead of creating a new one. The list of steps are as follows to create a Linux VM in Azure:- Create a resource group
- Create a subnet config
- Create a virtual network, set it up with the subnet config
- Create a public IP
- Create a security rule config to allow port 22 (SSH)
- Create a network security group nsg and add in the security rule config
- Create a network interface card nic and associate it with the public ip and the nsg
- Create a VM config and set the operating system, OS image and nic
- Create a VM config's SHH public key config
- Create a VM - Virtual Machine in Azure !
param([string]$resourceGroupName,
[string]$resourceGroupLocation,
[string]$vmComputerName,
[string]$vmUser,
[string]$vmUserPassword,
[string]$virtualNetworkName)
#Write-Host $resourceGroupName
#Write-Host $resourceGroupLocation
#Write-Host $vmComputerName
#Write-Host $vmUser
#Write-Host $vmUserPassword
# Definer user name and blank password
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString ' ' -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("azureuser", $securePassword)
New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name $resourceGroupName -Location $resourceGroupLocation
$subnetConfig = New-AzureRmVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig -Name default -AddressPrefix 10.0.0.0/24
$virtualNetwork = New-AzureRMVirtualNetwork -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name `
$virtualNetworkName -AddressPrefix 10.0.0.0/16 -Location $resourceGroupLocation `
-Subnet $subnetConfig
Write-Host "Subnet id: " $virtualNetwork.Subnets[0].Id
# Create a public IP address and specify a DNS name
$pip = New-AzureRmPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Location $resourceGroupLocation `
-Name "mypublicdns$(Get-Random)" -AllocationMethod Static -IdleTimeoutInMinutes 4
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 22
$nsgRuleSSH = New-AzureRmNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleSSH -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1000 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 22 -Access Allow
# Create a network security group
$nsg = New-AzureRmNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Location $resourceGroupLocation `
-Name myNetworkSecurityGroup -SecurityRules $nsgRuleSSH
# Create a virtual network card and associate with public IP address and NSG
$nic = New-AzureRmNetworkInterface -Name myNic -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Location $resourceGroupLocation `
-SubnetId $virtualNetwork.Subnets[0].Id -PublicIpAddressId $pip.Id -NetworkSecurityGroupId $nsg.Id
# Create a virtual machine configuration
$vmConfig = New-AzureRmVMConfig -VMName $vmComputerName -VMSize Standard_D1 | `
Set-AzureRmVMOperatingSystem -Linux -ComputerName $vmComputerName -Credential $cred -DisablePasswordAuthentication | `
Set-AzureRmVMSourceImage -PublisherName Canonical -Offer UbuntuServer -Skus 14.04.2-LTS -Version latest | `
Add-AzureRmVMNetworkInterface -Id $nic.Id
# Configure SSH Keys
$sshPublicKey = Get-Content "$HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
Add-AzureRmVMSshPublicKey -VM $vmconfig -KeyData $sshPublicKey -Path "/home/azureuser/.ssh/authorized_keys"
# Create a virtual machine
New-AzureRmVM -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Location $resourceGroupLocation -VM $vmConfig
We can then instantiate a new VM in Azure running the script above, which will create a standard D1 blade server in Azure
with approx. 3,5 GB RAM and 30 GB disk space with Ubuntu Server LTS latest from the publisher Canonical by calling this script
like for example:
./AzureVmCreate.ps1 -resourceGroupName "SomeResourceGroup" -resourceGroupLocation "northcentralus" "SomeVmComputer" -vmUser "adminUser" -password "s0m3CoolPassw0rkzzD" -virtualNetworkName "SomeVirtualNetwork"
After the VM is created, which for me took about 5 minutes time before the VM was up and running in Azure, you can access it by visiting the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com
You can then take notice of the public IP adress that the script in this article created and connect with : ssh azureuser@ip_address_to_linux_VM_you_just_created_in_Azure!
The following images shows me logging into the Ubuntu Server LTS Virtual Machine that was created with the Powershell core script in this article!
A complete list of available Linux images can be seen in the Azure marketplace or in the Microsoft Docs: Linux VMs in Azure overview
After installation, you can run the following cmdlet to clean up the resource group and all its resources, including the VM you created for testing.
Remove-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name myResourceGroup
Thursday, 9 August 2018
Detect USB drives in a WPF application
We can use the class System.IO.DriveInfo to retrieve all the drives on the system and look for drives where the DriveType is Removable. In addition, the removable drive (USB usually) must be ready, which is accessible as the property IsReady. First off, we define a provider to retrieve the removable drives:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
public static class UsbDriveListProvider
{
public static IEnumerable<DriveInfo> GetAllRemovableDrives()
{
var driveInfos = DriveInfo.GetDrives().AsEnumerable();
driveInfos = driveInfos.Where(drive => drive.DriveType == DriveType.Removable);
return driveInfos;
}
}
}
Let us use the MVVM pattern also, so we define a ViewModelbase class, implementing INotifyPropertyChanged.
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
public class ViewModelBase : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public void RaisePropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
if (PropertyChanged != null)
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
It is also handy to have an implemetation of ICommand:
using System;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
public class RelayCommand : ICommand
{
private Predicate<object> _canExecute;
private Action<object> _execute;
public RelayCommand(Predicate<object> canExecute, Action<object> execute)
{
_canExecute = canExecute;
_execute = execute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return _canExecute(parameter);
}
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute(parameter);
}
}
}
We also set the DataContext of MainWindow to an instance of a demo view model defined afterwards:
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
DataContext = new UsbDriveInfoDemoViewModel();
}
}
}
We then define the view model itself and use System.Management.ManagementEventWatcher to look for changes in the drives mounted onto the system.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Management;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
public class UsbDriveInfoDemoViewModel : ViewModelBase, IDisposable
{
public UsbDriveInfoDemoViewModel()
{
DriveInfos = new List<DriveInfo>();
ReloadDriveInfos();
RegisterManagementEventWatching();
TargetUsbDrive = @"E:<";
AccessCommand = new RelayCommand(x => true, x => MessageBox.Show("Functionality executed."));
}
public int UsbDriveCount { get; set; }
private string _targetUsbDrive;
public string TargetUsbDrive
{
get { return _targetUsbDrive; }
set
{
if (_targetUsbDrive != value)
{
_targetUsbDrive = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("TargetUsbDrive");
RaisePropertyChanged("DriveInfo");
}
}
}
public ICommand AccessCommand { get; set; }
private void ReloadDriveInfos()
{
var usbDrives = UsbDriveListProvider.GetAllRemovableDrives();
Application.Current.Dispatcher.Invoke(() =>
{
DriveInfos.Clear();
foreach (var usbDrive in usbDrives)
{
DriveInfos.Add(usbDrive);
}
UsbDriveCount = DriveInfos.Count;
RaisePropertyChanged("UsbDriveCount");
RaisePropertyChanged("DriveInfos");
});
}
public List<DriveInfo> DriveInfos { get; set; }
private ManagementEventWatcher _watcher;
private void RegisterManagementEventWatching()
{
_watcher = new ManagementEventWatcher();
var query = new WqlEventQuery("SELECT * FROM Win32_VolumeChangeEvent");
_watcher.EventArrived += watcher_EventArrived;
_watcher.Query = query;
_watcher.Start();
}
private void watcher_EventArrived(object sender, EventArrivedEventArgs e)
{
Debug.WriteLine(e.NewEvent);
ReloadDriveInfos();
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (_watcher != null)
{
_watcher.Stop();
_watcher.EventArrived -= watcher_EventArrived;
}
}
}
}
We also define a WPF multi-converter next to enable the button:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Data;
namespace TestPopWpfWindow
{
public class UsbDriveAvailableEnablerConverter : IMultiValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object[] values, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (values == null || values.Count() != 2)
return false;
var driveInfos = values[1] as List<DriveInfo>;
var targetDrive = values[0] as string;
if (driveInfos == null || !driveInfos.Any() || string.IsNullOrEmpty(targetDrive))
return false;
return driveInfos.Any(d => d.IsReady && d.Name == targetDrive);
}
public object[] ConvertBack(object value, Type[] targetTypes, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
And we define a GUI to test this code:
<Window x:Class="TestPopWpfWindow.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:TestPopWpfWindow"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525">
<Window.Resources>
<Style x:Key="usbLabel" TargetType="Label">
<Style.Triggers>
<DataTrigger Binding="{Binding IsReady}" Value="False">
<Setter Property="Background" Value="Gray"></Setter>
</DataTrigger>
<DataTrigger Binding="{Binding IsReady}" Value="True">
<Setter Property="Background" Value="Green"></Setter>
</DataTrigger>
</Style.Triggers>
</Style>
<local:UsbDriveAvailableEnablerConverter x:Key="usbDriveAvailableEnablerConverter"></local:UsbDriveAvailableEnablerConverter>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<TextBlock Text="USB Drive-detector" FontWeight="DemiBold" HorizontalAlignment="Center" FontSize="14" Margin="2"></TextBlock>
<TextBlock Text="Removable drives on the system" FontWeight="Normal" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="2"></TextBlock>
<TextBlock Text="Drives detected:" FontWeight="Normal" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="2"></TextBlock>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding UsbDriveCount, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" FontWeight="Normal" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="2"></TextBlock>
<ItemsControl Grid.Row="0" ItemsSource="{Binding DriveInfos, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
Width="100" BorderBrush="Black" BorderThickness="1">
<ItemsControl.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<Label Style="{StaticResource usbLabel}" Width="32" Height="32" FontSize="18" Foreground="White" Content="{Binding Name}">
</Label>
</StackPanel>
</DataTemplate>
</ItemsControl.ItemTemplate>
</ItemsControl>
</StackPanel>
<Button Grid.Row="1" Height="24" Width="130" VerticalAlignment="Top" Margin="10" Content="Access functionality" Command="{Binding AccessCommand}">
<Button.IsEnabled>
<MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource usbDriveAvailableEnablerConverter}">
<MultiBinding.Bindings>
<Binding Path="TargetUsbDrive"></Binding>
<Binding Path="DriveInfos"></Binding>
</MultiBinding.Bindings>
</MultiBinding>
</Button.IsEnabled>
</Button>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="2" Orientation="Horizontal" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Margin="2" Text="Target this USB-drive:"></TextBlock>
<TextBox Margin="2" Text="{Binding TargetUsbDrive, UpdateSourceTrigger=LostFocus}" Width="100"></TextBox>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Window>
I have now provided the Visual Studio 2013 solution with the code above available for download here:
Download VS 2013 Solution with source code above
Explore contents of a running container in Docker
This is a short tip how to explorer the contents of a running container in Docker.

Get Docker for windows from here: Docker for Windows First off, we can list our containers with the following command:
Note the CONTAINER ID value. Use this to explore the contents of the running container:
Note that in this example I just have to type the necessary part of the Guid of the CONTAINER ID to discern it from others and issue an exec command with the parameters -it (interactive and pseudo tty session) followed with bash. From now on, I can explore the container easily: ls -al The following image sums this up: Another cool tip, how about installing a new nginx web server on port 81 on your Windows Dev Box? Simple!
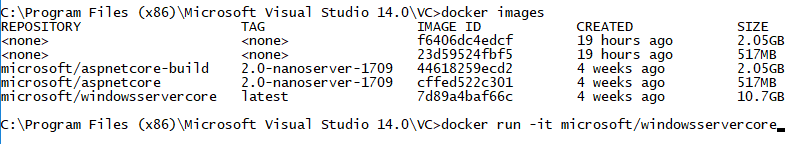
And the following command pulls a windowsservercore docker image (10,7 GB size) and starts it up and gives you a pseudo-terminal which is interactive:
docker run -it microsoft/windowsservercore

Get Docker for windows from here: Docker for Windows First off, we can list our containers with the following command:
docker container ls
Note the CONTAINER ID value. Use this to explore the contents of the running container:
docker exec -it 231 bash
Note that in this example I just have to type the necessary part of the Guid of the CONTAINER ID to discern it from others and issue an exec command with the parameters -it (interactive and pseudo tty session) followed with bash. From now on, I can explore the container easily: ls -al The following image sums this up: Another cool tip, how about installing a new nginx web server on port 81 on your Windows Dev Box? Simple!
docker run --detach publish 81:80 nginx
And the following command pulls a windowsservercore docker image (10,7 GB size) and starts it up and gives you a pseudo-terminal which is interactive:
docker run -it microsoft/windowsservercore

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




